Biomimetic Innovations Ltd R&D Engineer Antzela Tzagiollari and the research team at DCU recently published a paper titled;
‘Multi-objective property optimisation of a phosphoserine-modified calcium phosphate cement for orthopaedic and dental applications using design of experiments methodology.’
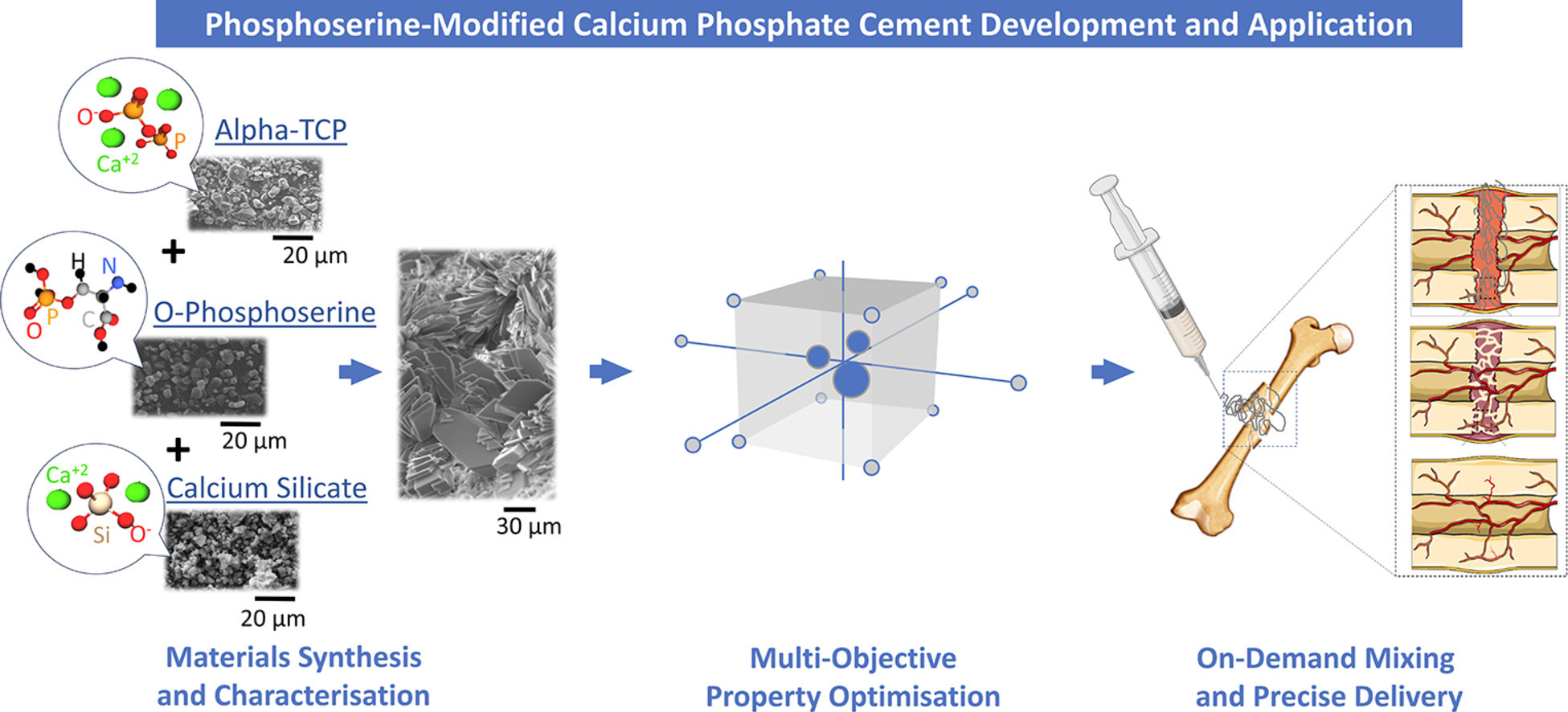
This publication explains how their DoE approach successfully optimised the composition of OsStic®, demonstrating that the liquid: powder ratio (LPR) and quantity of phosphoserine (wt%) significantly influences the material’s handling, mechanical and adhesion properties.
Subsequently, the DoE optimisation process identified the optimal formulation for OsStic®; demonstrating rapid setting, achieving complete solidification within 5 minutes, while also achieving high mechanical and adhesive properties (compressive strength of 29.2 ± 4.9 MPa and bond/shear strength of 3.6 ± 0.9 MPa).
Additional findings highlighted the ability of OsStic® to effectively support and stabilise bone fragments during the initial stages of natural bone healing; showing that this ground-breaking new material fulfils the clinical requirements for working and setting times, static mechanical, degradation properties, and injectability.
This further supports our belief that OsStic will enable surgeons to stabilise complex bone fractures; representing a significant advancement in treatment options, as well as the potential to greatly enhance patient outcomes.
Read the full publication here.